Introduction
Understanding the concept of equilibrium price is essential for anyone starting in business or finance. For beginners, this term may sound complex, but it simply refers to the price at which the quantity of a product demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers. When the market reaches this balance, there is no pressure for prices to rise or fall.
In this guide, we will explore what equilibrium price means, why it matters, and how it affects everyday decisions in business and the marketplace. Whether you are curious about pricing strategies, market trends, or just want a solid foundation in economics, this article will provide the clarity you need.
What is Equilibrium Price?
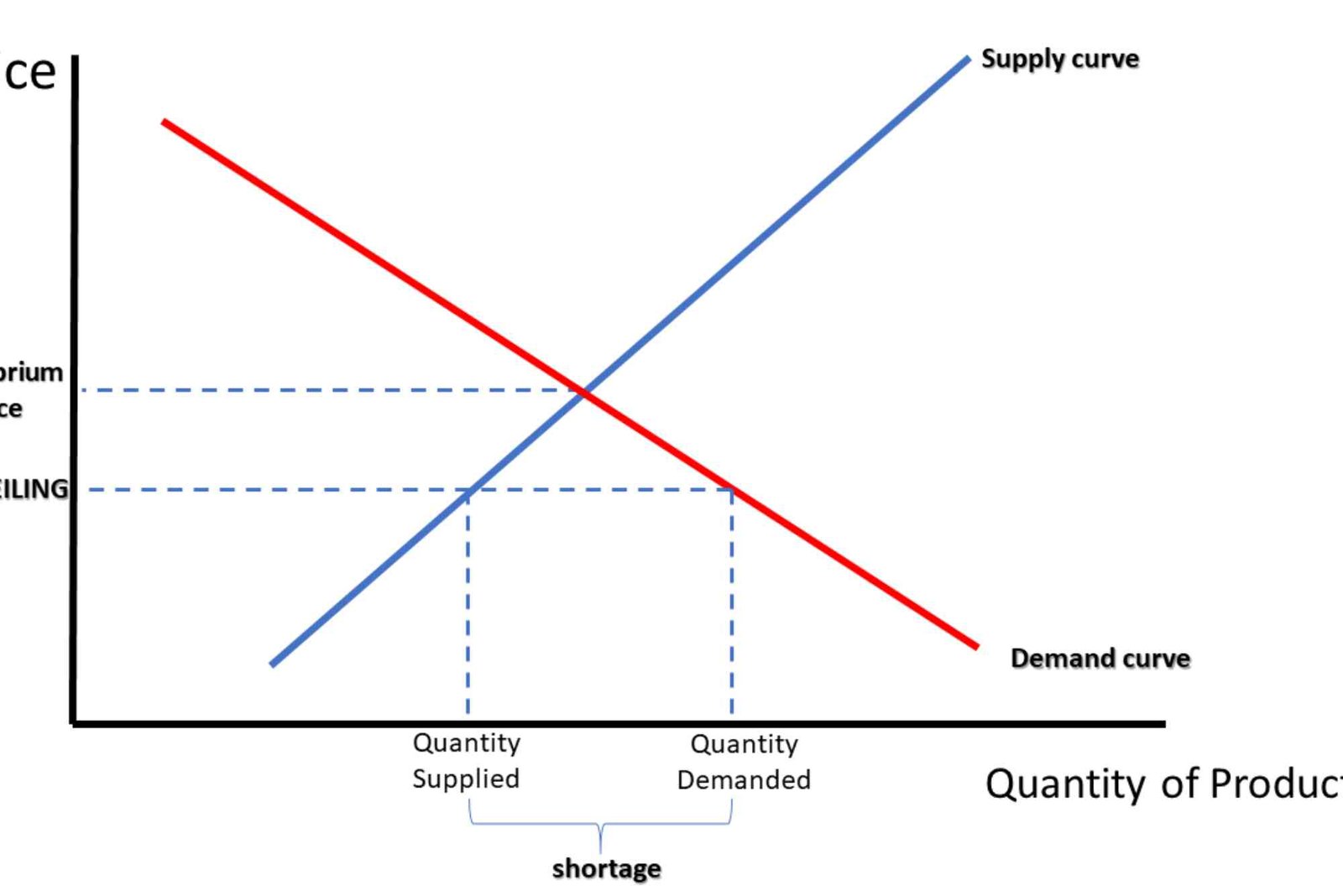
The equilibrium price is the point where supply and demand curves intersect. At this price, sellers are happy to sell, and buyers are happy to buy. This balance ensures that resources are allocated efficiently in a competitive market.
When the market price is above the equilibrium, there is a surplus of goods. Sellers may struggle to sell all their products, which can push the price down. Conversely, if the price is below equilibrium, there is a shortage, and buyers compete to get the limited goods, driving the price up.
Understanding this concept is crucial for small business owners, investors, and anyone learning about market dynamics. For a more detailed explanation, you can explore our guide to what is equilibrium price.
Why Equilibrium Price Matters
Equilibrium price is more than just an economic theory; it impacts real-world business decisions. For instance, retailers must understand pricing to avoid excess inventory or stockouts. Similarly, manufacturers use equilibrium pricing to plan production efficiently.
This concept also plays a role in consumer behavior. If prices are too high, consumers may delay purchases or switch to alternatives. If prices are too low, demand can exceed supply, creating scarcity. Recognizing the equilibrium helps maintain a healthy balance that benefits both buyers and sellers.
How Equilibrium Price is Determined
Supply and Demand Interaction
At its core, the equilibrium price depends on the interaction of supply and demand. Demand represents how much consumers want a product, while supply shows how much producers are willing to provide. Changes in either can shift the equilibrium. For example, a new technology may reduce production costs, increasing supply and potentially lowering the equilibrium price.
Market Adjustments
Markets naturally move toward equilibrium through adjustments. If a surplus exists, sellers reduce prices to attract buyers. If there is a shortage, buyers compete, pushing prices upward. These continuous adjustments help the market find a stable point where supply equals demand.
External Factors
Several external factors can influence equilibrium price. Economic growth, consumer preferences, and global trade dynamics all play a role. Even seasonal changes can shift demand and, consequently, the equilibrium price. Understanding these influences allows beginners to anticipate market movements and make informed decisions.
Real-Life Examples of Equilibrium Price
Consider a local farmers’ market. If the price of apples is too high, farmers may not sell all their stock. If the price is too low, buyers may rush to purchase, leaving some customers without apples. The equilibrium price is where the number of apples supplied matches the number of apples demanded.
Another example can be seen in online marketplaces. Products like smartphones often reach an equilibrium price as sellers compete for buyers, balancing supply and demand. Observing these patterns can provide practical insights into how equilibrium works in real life.
Common Misconceptions About Equilibrium Price
Many beginners assume that equilibrium price is static, but it is not. Markets are dynamic, and equilibrium shifts with changes in supply, demand, or external factors. Another misconception is that equilibrium price guarantees maximum profit. While it indicates market balance, businesses must still consider costs, competition, and strategy to remain profitable.
It’s also important to understand that equilibrium price does not mean all products are sold at the same price. Rather, it represents the overall market balance where supply and demand meet.
Equilibrium Price and Business Strategy
For business owners, knowing the equilibrium price is crucial. Setting prices too high can reduce sales, while pricing too low can erode profits. Companies often use market research and data analysis to estimate equilibrium and adjust strategies accordingly.
Understanding equilibrium also helps in forecasting and inventory management. Predicting demand and supply fluctuations allows businesses to maintain efficiency and avoid costly mistakes. This knowledge forms the foundation of many concepts in business & finance basics.
Equilibrium Price in Different Markets
Competitive Markets
In perfectly competitive markets, equilibrium price is determined entirely by supply and demand. No single buyer or seller can influence the market, making the concept straightforward for beginners to grasp.
Monopolistic Markets
In monopolistic markets, equilibrium price can be more complex. A single seller may influence prices, but demand still plays a crucial role. Understanding how equilibrium shifts in such markets can help beginners appreciate the dynamics of price control and competition.
Global Markets
Equilibrium price also applies to international trade. Exchange rates, tariffs, and global demand can affect supply and demand, shifting equilibrium. For those interested in economics or finance, observing these trends can provide valuable insights into global pricing patterns.
How to Calculate Equilibrium Price
Calculating equilibrium price involves comparing supply and demand equations. By setting quantity supplied equal to quantity demanded, you can solve for the equilibrium price. While the math may seem intimidating, understanding the principle behind it is simpler.
Beginners can start by plotting simple supply and demand curves and identifying the intersection point. This visualization helps illustrate how market forces interact and adjust over time.
For more technical details, you can refer to the finance definition resources available online.
Tips for Beginners
-
Observe local markets: Watch how prices fluctuate in grocery stores or online platforms.
-
Track supply and demand changes: Notice seasonal trends or product shortages.
-
Study market reports: Business news and reports provide real-world examples of equilibrium price shifts.
By following these tips, beginners can gradually develop a strong understanding of market pricing and equilibrium.
FAQs About Equilibrium Price
What is the difference between equilibrium price and market price?
Equilibrium price is the ideal balance point where supply equals demand. Market price can fluctuate above or below equilibrium due to temporary surpluses or shortages.
Why does equilibrium price change?
Changes in supply, demand, production costs, or external economic factors can shift equilibrium price. Seasonal variations also impact it.
How can businesses use equilibrium price?
Businesses use equilibrium price to optimize pricing strategies, manage inventory, and forecast demand efficiently.
Is equilibrium price the same for all products?
No, each product has its own equilibrium based on its market supply and demand conditions.
Can equilibrium price guarantee profit?
Not necessarily. It indicates market balance, but businesses must account for costs and strategy to ensure profitability.
For beginners, understanding equilibrium price is a fundamental step in learning how markets function. By grasping this concept, you can make informed decisions in business, investing, and everyday purchases. Observing market trends and analyzing supply and demand helps beginners recognize equilibrium in real-world scenarios.
Take the next step in your financial learning journey and deepen your knowledge of market dynamics through our guide to what is equilibrium price. Explore resources in business & finance basics to enhance your understanding further.