Introduction
Understanding the concept of equilibrium price is essential for anyone navigating the world of business and finance. This price is where the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of a product are equal, resulting in market stability. Whether you are a student, entrepreneur, or investor, knowing how to identify and analyze equilibrium price can significantly enhance your decision-making skills. In this step-by-step guide, we provide a comprehensive checklist to help you grasp the concept with clarity. To learn more about what is equilibrium price, continue reading.
What Is Equilibrium Price?
Equilibrium price is the market price at which the quantity of a product buyers want to purchase equals the quantity sellers want to sell. At this price, there is no surplus or shortage, creating a balanced market environment. The concept originates from fundamental economic principles and plays a vital role in pricing strategies, financial forecasting, and market analysis.
Key Features of Equilibrium Price
Equilibrium price has several defining characteristics. First, it represents a stable market point where supply equals demand. Second, it changes only when there are shifts in supply or demand. Third, it ensures optimal allocation of resources, preventing market inefficiencies.
Checklist to Identify Equilibrium Price
Analyze Market Demand
Understanding demand is the first step. Examine how much consumers are willing to buy at various price levels. Consider factors like consumer preferences, income levels, and market trends. Tools such as demand curves and historical data can help you visualize demand patterns accurately.
Examine Market Supply
Supply analysis involves evaluating how much producers are willing to sell at different prices. Factors influencing supply include production costs, technology, and availability of resources. Using supply curves, you can predict how changes in production impact the equilibrium price.
Plot Demand and Supply Curves
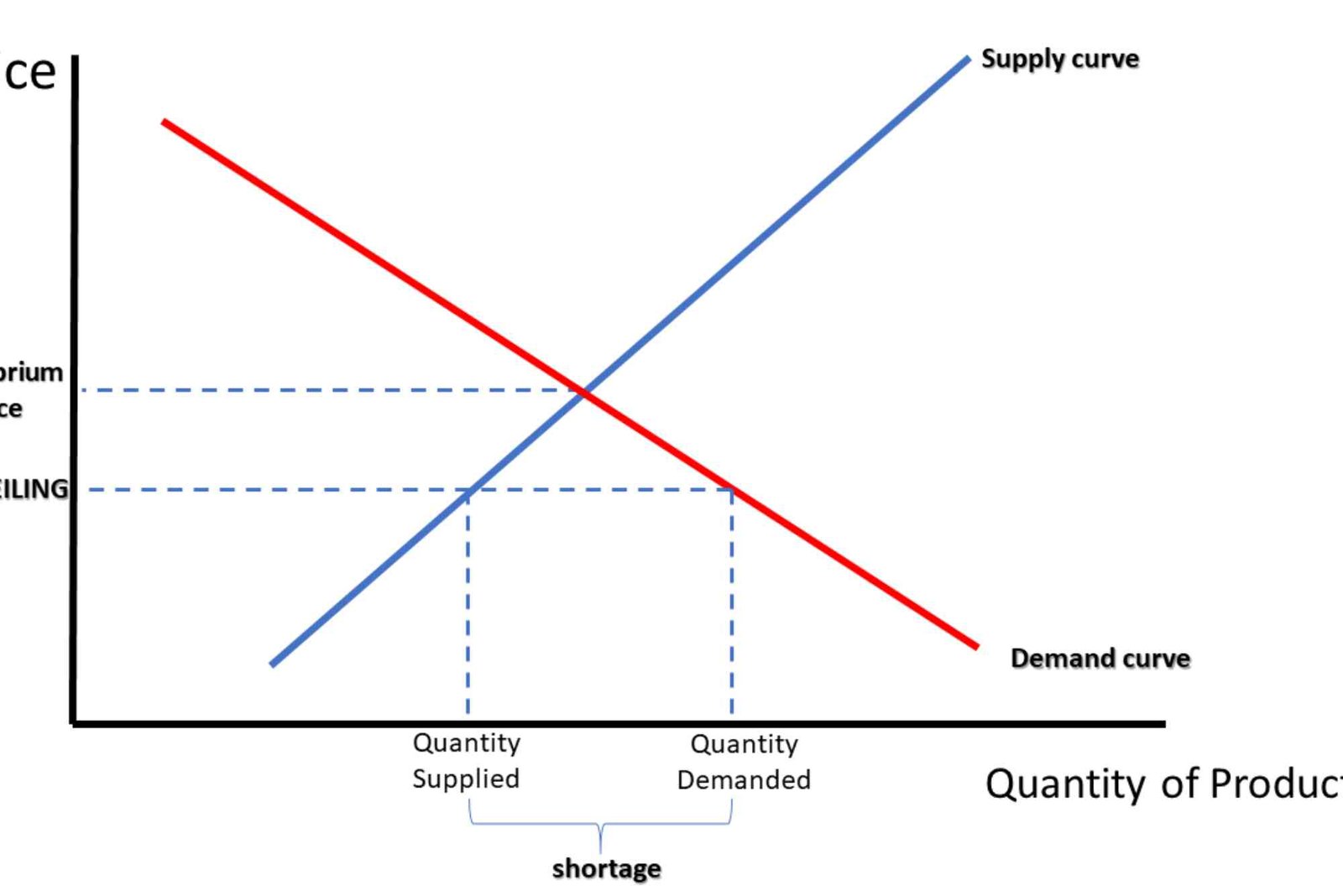
Graphically representing demand and supply curves is crucial. The intersection of these curves indicates the equilibrium price. This visual approach makes it easier to understand market dynamics and anticipate shifts caused by external factors.
Determine Market Equilibrium
Once the curves are plotted, locate the intersection point. This point represents the equilibrium price and the corresponding quantity. It shows where market forces balance, ensuring that no surplus or shortage exists. Understanding this helps in strategic pricing and inventory management.
Monitor Market Changes
Markets are dynamic, and equilibrium prices fluctuate with changes in demand or supply. Regularly monitor factors such as consumer trends, input costs, and economic conditions. Adapting to these changes ensures that your pricing strategy remains effective and competitive.
Apply Equilibrium Insights
Use equilibrium price insights to guide business decisions. Set optimal pricing, forecast sales, and adjust production levels. This step is particularly important for entrepreneurs and investors looking to maximize profitability and minimize losses. For broader financial context, explore business & finance basics and finance definition.
Importance of Equilibrium Price in Business
Equilibrium price is more than a theoretical concept; it has practical applications. Businesses use it to determine fair pricing, avoid overproduction, and manage resources efficiently. Investors analyze equilibrium to forecast market trends and assess risk. Policymakers also use it to implement price controls and stabilize markets.
How Equilibrium Price Affects Consumers
For consumers, equilibrium price ensures affordability and availability of goods. When prices are too high, demand drops, leading to adjustments. Conversely, if prices are too low, shortages occur, prompting market correction. Understanding this dynamic helps consumers make informed purchasing decisions.
How Equilibrium Price Guides Producers
Producers rely on equilibrium price to plan production and inventory. Accurate pricing reduces waste, maximizes profits, and enhances competitiveness. Businesses that monitor equilibrium prices can respond proactively to market fluctuations.
Even experienced professionals can make errors when analyzing equilibrium price. One common mistake is ignoring market trends and external factors. Another is relying solely on historical data without considering consumer behavior shifts. Avoid these pitfalls to ensure accurate analysis and better decision-making.
Equilibrium price is a cornerstone of economic theory and practical business strategy. By following this step-by-step checklist, you can identify, analyze, and apply equilibrium price effectively. Whether for pricing products, forecasting trends, or managing resources, mastering this concept strengthens your financial acumen. Start using these insights today to make smarter business decisions. To dive deeper, learn more about what is equilibrium price.
FAQs
What is the difference between equilibrium price and market price?
Equilibrium price is where supply equals demand, while market price can fluctuate due to temporary imbalances.
How does a shift in demand affect equilibrium price?
An increase in demand raises the equilibrium price and quantity, while a decrease lowers both.
Can equilibrium price change over time?
Yes, changes in supply, demand, production costs, or external economic factors can shift the equilibrium price.
Why is equilibrium price important for businesses?
It helps businesses optimize pricing, manage inventory, and predict market trends effectively.
Where can I find more information on finance concepts?
You can explore comprehensive finance definitions for further learning.